Organ-on-Chip (OOC) are tiny chip-like structures with specific embedded cells, they mimic the key functions of an organ in miniature formats outside the body.
LONDON, GREATER LONDON, UK, June 9, 2016 /EINPresswire.com/ — “Universities are the centres for the discovery and development of OOCs. Scientific experts and researchers at universities or institutes have been responsible for designing breakthrough OOC models(http://goo.gl/kQ4WGb). In order for the models to move to the next stage of commercialization, they need to be backed up by a valid proof of concept”
1. Introduction
OOCs are microfluidic 3D cell culture devices that closely mimic the key physiological functions of body organs. An OOC is also referred to as a biomimetic microsystem or 3D microphysiologic platform.
OOCs are one of the most exciting multidisciplinary areas of scientific research(http://goo.gl/kQ4WGb). They have the distinguishing characteristic of emulating the human micro environment in vitro, which is not possible by any other conventional in-vitro techniques. This unique feature of an OOC is the result of integrating biology with technology.
Scientific advances in cell biology, microfabrication and microfluidics have led to the development of OOCs. They are tiny chip-like structures with specific embedded cells. The combination of chip and cells in the presence of suitable conditions mimic the key functions of an organ in miniature formats outside the body.
Alternative in-vitro techniques, in particular 2D and 3D conventional cell culture techniques, are based on non-live cell lines. Unlike these models, OOCs are seeded with living human cells. This particular feature makes them far superior to conventional models which fail to simulate the human in-vivo environment. In-vivo animal models(http://goo.gl/kQ4WGb) as well as non-live cells are not considered as the best models to simulate the key physiological functions of human organs, primarily due to genetic variations. Thus there has arisen a need for a biomimetic model which can exactly predict the effects of a drug molecule on humans. OOC models are therefore considered as the next wave of cell culture techniques for drug discovery and development.
2. Product Analysis
This section gives a general overview on Organ-on-Chips (OOCs) and information on designs and techniques(http://goo.gl/kQ4WGb) used for manufacturing these devices. Details about various organ-specific models are also provided. Technical Description
OOC are microfluidic devices with hollow micrometer sized chambers seeded with living cells. The tiny chambers are continuously perfused with a suitable medium which acts as a blood surrogate. OOCs are not designed to represent an entire body organ but are created to simulate key tissue- and organ-level functions in vitro.
Typical Organ-on-Chip Structure displays the structure of a typical OOC(http://goo.gl/kQ4WGb) and a multiwell cell culture platform which is used to create organ models by leveraging microfluidics.
OOC models vary in design and approach from one research project to another. They are designed by research scientists as transparent chips about the size of a memory stick; they may also be created on specialised microtiter/multiwell plates by other scientific experts.
2.1 Product Design Materials
The chips are generally made of synthetic polymers. Transparent polymers are generally preferred as they allow embedded cells(http://goo.gl/kQ4WGb) to be viewed through a microscope during the experiment. Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS), a silicon-based organic polymer, is a material of choice for designing OOCs as it is highly flexible, optically clear, non-toxic and non-flammable. However, PDMS possesses the major drawback of absorbing hydrophilic small molecules. This property of PDMS can alter the experimental procedures.4 For this reason, many key players in the OOC market have developed their own proprietary polymers for designing OOCs.
3. Market Characteristics
3.1 Organ-on-Chip Origin
A drug needs to undergo several tests, in animals and humans, in order to get approved. Before testing of a drug molecule on human volunteers it undergoes initial screening tests in laboratories, followed by testing in animals(http://goo.gl/kQ4WGb). These initial steps are known as preclinical tests which develop adequate data to underpin a decision that it is reasonably safe to proceed with human trials of the drug.
Therefore laboratory tests or in vitro cell-based assay is an essential part of drug screening and development process. However, until now none of the conventional in vitro cell culture techniques could eliminate a large proportion of unsuitable compounds at the early stages of drug screening. This fundamental drawback of conventional cell culture techniques(http://goo.gl/kQ4WGb) gave rise to the concept of simulating the physiological environment of body organs in vitro. OOC has the ability to predict the properties of a drug molecule and provide details of the effects which it can produce on body organs.
3.2 Organ-on-Chip Features
The design and development of an OOC is made possible by using the relevant novel techniques from cell biology, microfabrication, microfluidics, material science and nanotechnology. The specific chip design(http://goo.gl/kQ4WGb) varies based on manufacturing techniques and the organ it simulates, although the basic structure usually remains the same.
An OOC is a distinctive model which possesses some features which are the basis for its high physiological resemblance with body organs. Unique features of an OOC include:
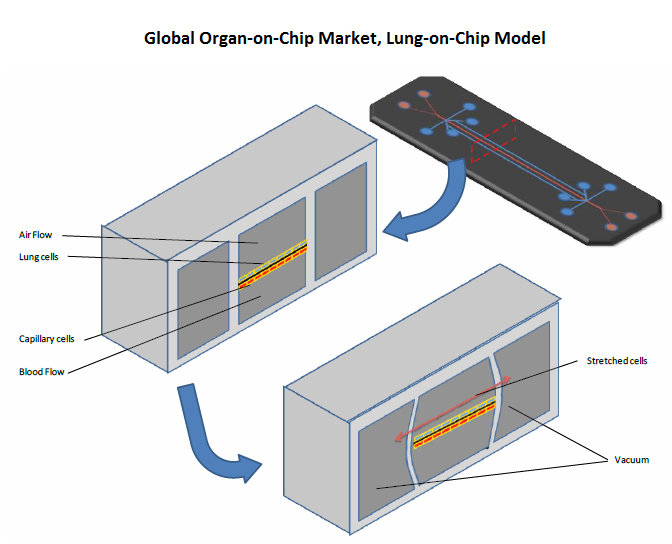
• Differentiation of tissue-to-tissue interfaces such as the interface between a pulmonary epithelium tissue and a capillary tissue
• Spatiotemporal gradients of chemicals across different cells with a tissue and between two tissues
• Mechanically active microenvironments such as vasoconstriction and vasodilator responses of blood vessels based on temperature differentials. These features of OOC make it superior to other in vitro techniques.
3.3 Organ-on-Chip Applications
Applications For OOCs In The Healthcare Industry
OOCs can be used in every aspect of drug discovery and development, but currently these chips are more commonly being used for preclinical ADME/Tox testing and for lead identification(http://goo.gl/kQ4WGb). Although still in the early stages of development, other potential applications of OOCs in the healthcare industry include –
i. Disease Modelling –
Disease modelling includes development of a disease or infection artificially by infusion of pathogens on a chip model, which is then examined for changes which occur at cellular and tissue-levels. This method mainly helps identify the drug molecules(http://goo.gl/kQ4WGb) which can either counteract or stop the undesired mechanisms that lead to disease.
ii. Patient Stratification –
Patient stratification is a relatively new area of healthcare which helps to differentiate diseased patients into specific sub-groups. For instance, OOC models can help categorize breast cancer patients(http://goo.gl/kQ4WGb) who are resistant to platinum chemotherapy. This stratification helps physicians to prescribe therapies that have the best therapeutic effect on patients.
iii. Phenotypic Screening –
Phenotypic screening is used in biological research and drug discovery to identify substances such as small molecules, peptides, or RNAi that alter the phenotype of a cell or an organism in a desired manner.
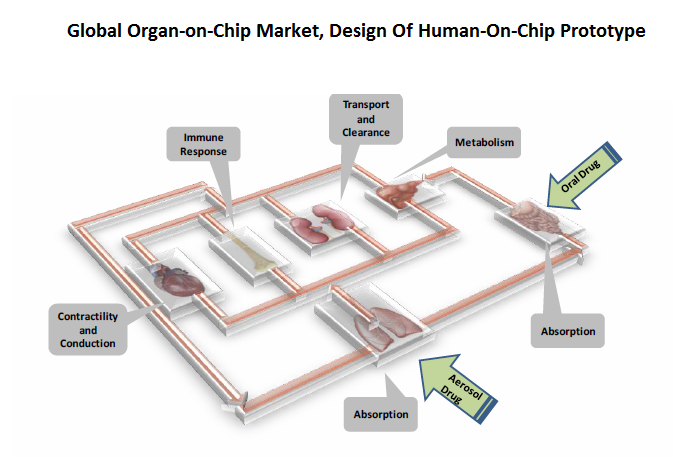
“Many research institutes are combining existing OOC models into an integrated system called a human-on-chip. It combines more than 10 organs into one single chip and so allows assessment of drug effects in all organs of the body. The Department of Biological Engineering at MIT and the Wyss Institute for Biologically Inspired Engineering at Harvard University(http://goo.gl/kQ4WGb) are two teams which have been granted $37 million and $32 million, respectively, from The USA’s National Institute of Health (NIH) and Defense Advanced Research Projects’ Agency (DARPA) for developing human-on-chip platforms”
4. Market Segmentation
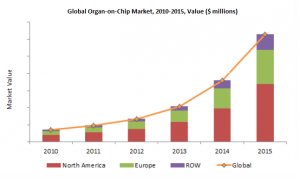
North America accounted for about 50% of the global market for OOC devices in 2015. The USA accounts for the dominant share of the North American market. The presence in this region of several potential end users, including the major pharmaceutical giants Pfizer, GlaxoSmithKline, Johnson and Johnson, and major research organizations makes it account for a large part of the global market. The provision of high-scale funding(http://goo.gl/kQ4WGb) by several US government organizations including National Institutes of Health (NIH) and Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) also supports research in the USA.
Funding provided by NIH in associations with DRAPA and Food and Drug Administration (FDA) through the ‘Tissue Chip for Drug Screening’ initiative was also a key driver of the OOC market in the USA during the historic period(http://goo.gl/kQ4WGb). The initiative, which was launched in 2012, initially focused on providing funds for development of OOC models that mimic human biological functionality and responses.
Europe accounted for 40% of the global OOC market in 2015. The presence of multiple key OOC players including Mimetas, CN Bio and Tissuse makes it occupy a significant share of the global market. Grants provided by several government and non-government agencies(http://goo.gl/kQ4WGb) also support the scope of research and development of new OOC models in this region.
The market for OOC is currently not well established in ROW in comparison with North America and Europe. However, the presence of potential end-users which can tap the new technology for their research needs makes these regions contribute a notable share in the global OOC market. Japan, China and Australia are among the top contributors to the OOC market in the ROW.
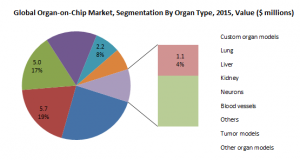
4.1 Custom Organ Models
Several organ-specific OOC models are being commercialized. Some of the organ-on-chip platforms designed by companies such as Mimetas, CN Bio and TissUse can be modified according to the experimental requirements. Some of the models have the ability to integrate two-organ models(http://goo.gl/kQ4WGb) on a single platform. These custom models are of great importance especially for pre-clinical screening of drug molecules during the early stages of product development.
4.2 Lung
The lung-on-chip is one of the most commercially used organ models. It constituted 19% of the global OOC market in 2015. Lung-on-chip is mainly used to study airway closure and opening, lung inflammation(http://goo.gl/kQ4WGb), airway protein synthesis or pulmonary absorption.
4.3 Liver
Liver-on-chip is one of the most versatile organ models available commercially. It accounted for 17% of the global OOC market in 2015. It is mainly used for toxicology testing of drugs. Some liver disease models(http://goo.gl/kQ4WGb) are also commercially available such as CN-Bio’s Quantam-B, a hepatitis-B model. The specific disease models on chips can be used for screening and evaluation of drug molecules for specific diseases.
4.4 Kidney
Kidney-on-chip is another organ model with a notable commercial presence. In 2015 it constituted 15% of the global OOC market. It is mainly used to test the toxic effects of drugs on the kidneys and also to evaluate the important pharmacokinetic parameters and elimination characteristics, of a drug molecule.
4.5 Neurons
Neuron-on-chip models accounted for 8% of the global OOC market in 2015. These models mainly predict the toxic effects of drugs on the complex neurological network. Models of neurological diseases such as multiple sclerosis, Parkinson’s disease and Alzheimer’s disease are employed for drug discovery and toxicity screening.
5. Market Drivers And Restraints
Drivers
Government Funding Drives The Market For Organ-on-Chips – The USA’s National Institutes of Health (NIH) established a ‘Tissue Chip for Drug Screening’ initiative in 2012. The establishment of this program was aided by NIH’s Common Fund and the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke. The NIH plans to commit up to $70 million over five years for the program. In total, 15 NIH institutes and centres are assisting in the coordination of this program. NIH, in collaboration with the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA)(http://goo.gl/kQ4WGb) and the Food and Drug Administration (FDA), is leading this initiative.
Restraints
Complex Manufacturing Techniques Are A Restraint On Organ-on-Chip Market Growth – OOC manufacture involves complex processes which can be a restraint on the global OOC market.
Regulatory Hurdles For Drug Approvals – Stringent drug regulatory processes are a major restraint for the widespread use of OOC devices by pharmaceutical companies. Drug regulatory authorities scrutinize the preclinical and clinical investigational data of a drug molecule(http://goo.gl/kQ4WGb) to validate and approve it. The data generated by testing the drug in animal models and humans are required for the drug approval process.
6. Competitive Landscape
Only a few companies are developing OOCs. Each spinoff company maintains and follows its own proprietary methodologies for designing and manufacturing OOCs. The level of competition amongst these few players is moderate. Each is involved in robust RD activities to innovate new models of OOC. As a result competition is likely to intensify in the coming years. There are also likely to be new spinoff companies(http://goo.gl/kQ4WGb) from the universities.
Buy Now
• Organ-On-Chip Global Market Report is a detailed report giving a unique insight into this market. The report is priced at $4000 for an individual user. To use across your office the price is $6000 and $8000 if you wish to use across a multinational company.
• Clients are able to input on the design of the report and highlight points of special interest.
About The Business Research Company
Visit TheBusinessResearchCompany.com or call +447443439350 or +918897263534 for more information on this and many other titles.
The Business Research Company is a market research and intelligence company which excels in company, market and consumer research. It has research professionals at its offices in the UK, India and the US as well a network of trained researchers globally. It has specialist consultants in a wide range of industries including manufacturing, healthcare, financial services and technology.
The Business Research Company’s management have more than 20 years of varied business research experience. They have delivered hundreds of research projects to the senior management of some of the world’s largest organizations.
The Business Research Company’s Consultants have master’s qualifications from top institutes and include MBAs, MSCs, CFAs and CAs. The Business Research Company’s Consultants gain training and qualifications from the Market Research Society and are trained in advanced research practices, techniques, and ethics.
Dinesh Kumar
The Business Research Company
+918897263534
email us here